Baker's Cyst Aspiration
Equipment and Medications
|
|

Equipment 
Medications |
Procedure Instructions:
| Instructions | |
| 1. Standard pre-procedure workup (obtain consent, check indications and contraindications, check allergies). Review any relevant imaging | |
| 2. Position patient prone. | Picture of probe on patient when prone |
| 3. Pre-procedure images to identify optimal path. Ideally, place probe in transverse plane. | |
| 4. Mark needle site and ideal probe location. | |
| 5. Prep patient; betadine or chlorhexidine x 3. Clear wide area. | |
| 6. Place sterile drape. | |
| 7. Draw up medications as listed in equipment list. | |
| 8. Place a wheal underneath the skin using a 25g needle with the 1% lidocaine at the site marked for the needle. With ultrasound guidance place the 1% lidocaine deeper within the subcutaneous tissues, taking care not to breach the Baker's cyst. | |
| 9. Once numb, exchange the 25g needle for an 18g needle. | |
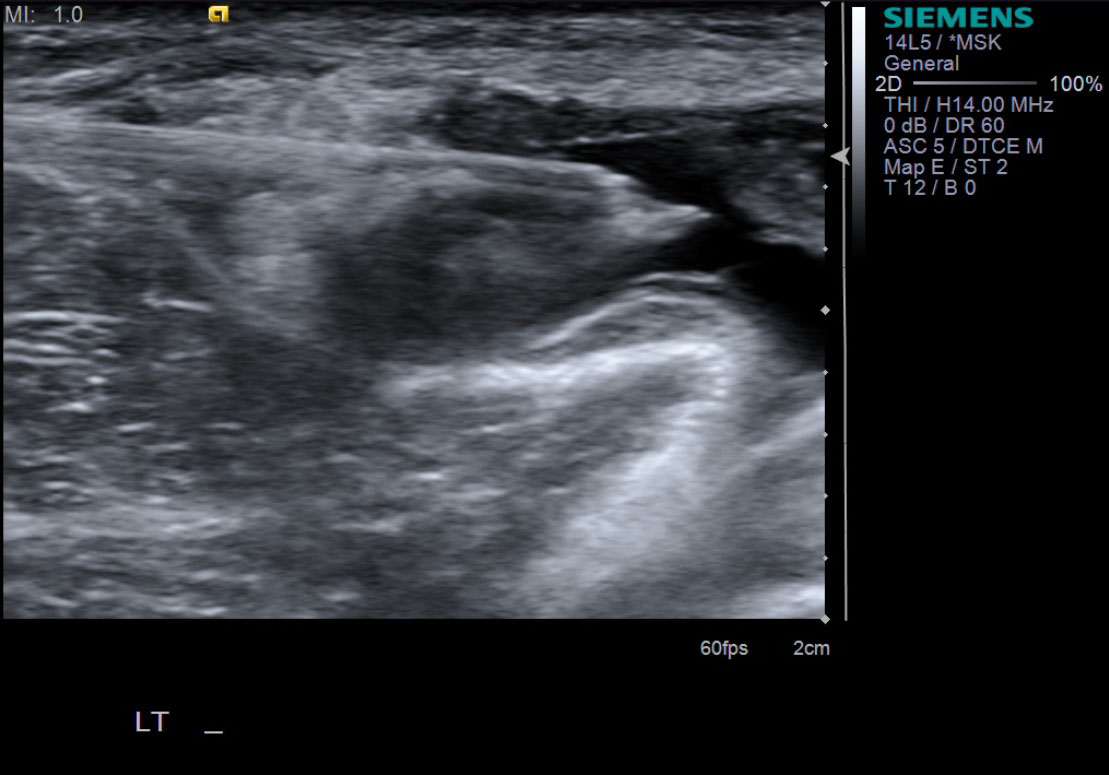
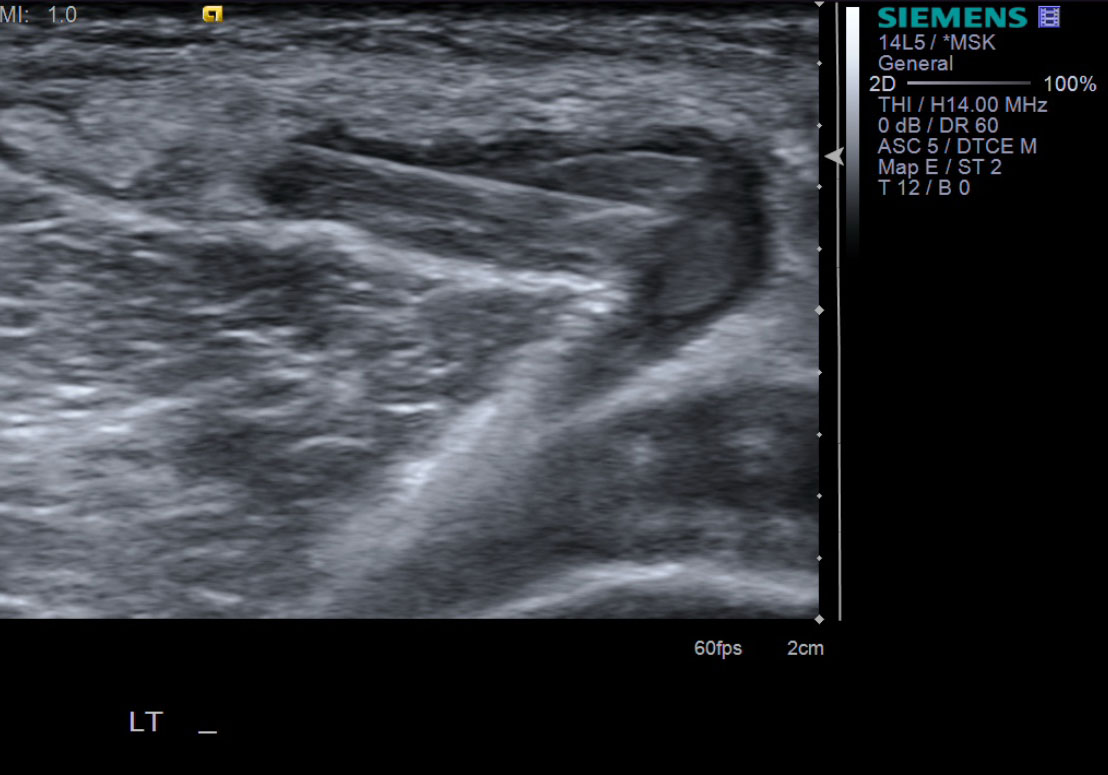
| 10. With ultrasound guidance, advance the 18g needle into the Baker's cyst. | |
| 11. Place the 10cc syringe on the end of the 18g needle. | |
| 12. While watching under ultrasound, aspirate almost the entirety of the Baker's cyst. Often the fluid is thick and gelatinous. Therefore, spinning the needle or bobbing it back and forth may help aspirate the majority of the fluid. | |
| 13. Exchange the 10cc syringe containing the aspirated fluid, with the 3cc syringe containing the steroid/anesthetic concoction listed in step 7. Inject the 3cc's into the cyst cavity. |
|
| 14. Take sonographic images documenting the reduction in size of the Baker's cyst. |
 Aspirated cyst fluid |
| 15. Follow standard post-procedure protocol with cleaning off the skin and placing a bandage. |
References
- Zwar, Read, and Noakes. "Sonographically Guided Glenohumeral Joint Injection." AJR July 2004 vol. 183 no. 148-150.